 login/create account
login/create account
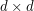 generic matrix?
generic matrix? For simplicity say we work over the complex numbers. The 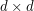 generic matrix is the matrix with entries
generic matrix is the matrix with entries 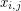 for
for 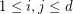 . Its determinant is a homogeneous form of degree
. Its determinant is a homogeneous form of degree 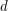 , in
, in 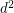 variables. If
variables. If 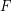 is a homogeneous form of degree
is a homogeneous form of degree 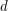 , a power sum expression for
, a power sum expression for 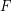 is an expression of the form
is an expression of the form 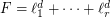 , the
, the 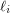 (homogeneous) linear forms. The Waring rank of
(homogeneous) linear forms. The Waring rank of 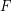 is the least number of terms
is the least number of terms  in any power sum expression for
in any power sum expression for 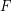 . For example, the expression
. For example, the expression 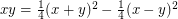 means that
means that 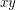 has Waring rank
has Waring rank 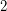 (it can't be less than
(it can't be less than 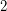 , as
, as 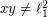 ).
).
The 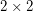 generic determinant
generic determinant 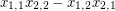 (or
(or 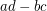 ) has Waring rank
) has Waring rank  . The Waring rank of the
. The Waring rank of the 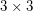 generic determinant is at least
generic determinant is at least 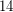 and no more than
and no more than 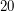 , see for instance Lower bound for ranks of invariant forms, Example 4.1. The Waring rank of the permanent is also of interest. The comparison between the determinant and permanent is potentially relevant to Valiant's "VP versus VNP" problem.
, see for instance Lower bound for ranks of invariant forms, Example 4.1. The Waring rank of the permanent is also of interest. The comparison between the determinant and permanent is potentially relevant to Valiant's "VP versus VNP" problem.
Bibliography
* indicates original appearance(s) of problem.

 Drupal
Drupal CSI of Charles University
CSI of Charles University