 login/create account
login/create account
Homomorphisms
Cores of Cayley graphs ★★
Author(s): Samal
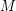 be an abelian group. Is the core of a Cayley graph (on some power of
be an abelian group. Is the core of a Cayley graph (on some power of 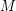 ) a Cayley graph (on some power of
) a Cayley graph (on some power of 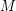 )?
)? Keywords: Cayley graph; core
Pentagon problem ★★★
Author(s): Nesetril
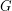 be a 3-regular graph that contains no cycle of length shorter than
be a 3-regular graph that contains no cycle of length shorter than 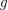 . Is it true that for large enough~
. Is it true that for large enough~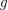 there is a homomorphism
there is a homomorphism 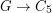 ?
? Keywords: cubic; homomorphism
Mapping planar graphs to odd cycles ★★★
Author(s): Jaeger
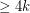 has a homomorphism to
has a homomorphism to 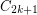 .
. Keywords: girth; homomorphism; planar graph
Weak pentagon problem ★★
Author(s): Samal
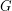 is a cubic graph not containing a triangle, then it is possible to color the edges of
is a cubic graph not containing a triangle, then it is possible to color the edges of 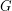 by five colors, so that the complement of every color class is a bipartite graph.
by five colors, so that the complement of every color class is a bipartite graph. Keywords: Clebsch graph; cut-continuous mapping; edge-coloring; homomorphism; pentagon
Algorithm for graph homomorphisms ★★
Author(s): Fomin; Heggernes; Kratsch
Is there an algorithm that decides, for input graphs 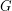 and
and 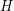 , whether there exists a homomorphism from
, whether there exists a homomorphism from 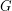 to
to 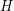 in time
in time 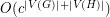 for some constant
for some constant  ?
?
Keywords: algorithm; Exponential-time algorithm; homomorphism
Circular choosability of planar graphs ★
Author(s): Mohar
Let 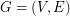 be a graph. If
be a graph. If 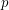 and
and 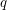 are two integers, a
are two integers, a 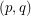 -colouring of
-colouring of 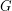 is a function
is a function  from
from 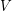 to
to 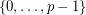 such that
such that 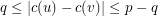 for each edge
for each edge 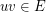 . Given a list assignment
. Given a list assignment 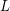 of
of 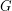 , i.e.~a mapping that assigns to every vertex
, i.e.~a mapping that assigns to every vertex  a set of non-negative integers, an
a set of non-negative integers, an 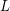 -colouring of
-colouring of 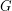 is a mapping
is a mapping 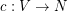 such that
such that 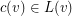 for every
for every 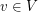 . A list assignment
. A list assignment 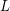 is a
is a 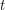 -
-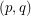 -list-assignment if
-list-assignment if 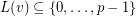 and
and 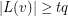 for each vertex
for each vertex 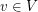 . Given such a list assignment
. Given such a list assignment 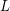 , the graph G is
, the graph G is 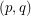 -
-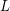 -colourable if there exists a
-colourable if there exists a 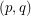 -
-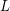 -colouring
-colouring  , i.e.
, i.e.  is both a
is both a 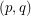 -colouring and an
-colouring and an 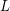 -colouring. For any real number
-colouring. For any real number 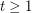 , the graph
, the graph 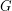 is
is 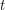 -
-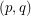 -choosable if it is
-choosable if it is 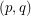 -
-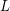 -colourable for every
-colourable for every 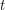 -
-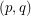 -list-assignment
-list-assignment 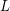 . Last,
. Last, 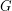 is circularly
is circularly 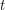 -choosable if it is
-choosable if it is 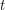 -
-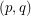 -choosable for any
-choosable for any 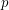 ,
, 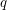 . The circular choosability (or circular list chromatic number or circular choice number) of G is
. The circular choosability (or circular list chromatic number or circular choice number) of G is 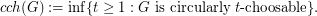
Keywords: choosability; circular colouring; planar graphs

 Drupal
Drupal CSI of Charles University
CSI of Charles University